You’re likely running one of two kinds of operations right now: one where your team spends hours on repetitive tasks that don’t move the needle—data entry, lead qualification, invoice processing, email follow-ups—or you’re already feeling the competitive pressure from companies that have figured out how to eliminate this friction.
AI automation isn’t a luxury anymore. It’s the difference between scaling fast and scaling frustrated. By 2025, 75% of B2B sales organizations are implementing AI to increase efficiency and profitability. But here’s what most companies get wrong: they treat AI automation the same way they treated earlier automation tools, expecting it to just follow rules. AI does something fundamentally different. It learns, adapts, and makes decisions—turning your repetitive workflows into intelligent systems that get smarter with time.
What “AI automation for B2B” actually means
AI automation for B2B means teaching software to handle tasks that usually require human judgment. Instead of telling a system “if lead score is above 50, send email,” you’re giving it historical data on which leads actually convert and letting it learn the patterns that predict a sale. The system updates those patterns continuously—it gets smarter as it learns.
Think of it this way: traditional automation is like a stoplight that only knows red and green. AI automation is like a traffic management system that watches actual traffic patterns, predicts congestion, and adjusts signals in real time.
Why traditional automation is no longer enough
Rule-based automation works great for straightforward processes: “If invoice arrives, extract these three fields, route to approval.” Simple. Clean. Predictable. But most B2B operations aren’t simple. Your leads come from different sources with inconsistent data. Your customer issues vary widely. Your decision-making relies on context and history, not just rules.
When you try to automate these complex processes with traditional automation, you end up creating massive rule sets that break the moment something unexpected happens. AI handles that nuance naturally. It processes unstructured data—emails, chat messages, documents in different formats—and makes sense of context.
The shift from rule-based automation → intelligent automation
The evolution looks like this:
-
Rule-based automation: Follow explicit instructions (if X, then Y)
-
Traditional automation tools: Chain together multiple if-then rules to handle more complex workflows
-
Intelligent automation (AI automation): Learn patterns from data, predict outcomes, adapt as conditions change, handle exceptions automatically
For B2B companies, this shift matters because your business processes are complex, data-heavy, and constantly changing. Intelligent automation scales with that complexity instead of breaking under it.
Who this guide is for
If you’re a founder trying to scale without hiring 15 new people, a sales leader managing forecasts across multiple pipelines, an operations director managing invoices and vendor data, a marketing manager trying to personalize campaigns at scale, or a customer success leader overwhelmed with support tickets—this guide is built for you. We’ll skip the hype and focus on what actually works, how much it costs, how long it takes, and what results you can realistically expect.
What Is AI Automation for B2B?
AI automation vs traditional automation
The clearest way to understand the difference: traditional automation executes instructions. AI automation makes decisions.
Traditional automation: “When an invoice PDF arrives, extract invoice number, vendor name, and total amount using OCR, then route to [email protected].”
AI automation: “Analyze this invoice and every similar invoice we’ve processed, understand vendor patterns, cross-reference with purchase orders, flag discrepancies, predict payment terms, check for duplicate invoices, and route to the right person based on amount and vendor relationship.”
Traditional automation is faster to set up—sometimes just days. But it breaks when data doesn’t match expected patterns. AI automation takes longer to implement but handles the messiness of real-world data.
How AI makes automation adaptive, not just repetitive
Here’s the mechanism: every time an AI automation system processes a task, it collects feedback. When that SaaS product demo actually converts a lead, the AI system learns. When a support ticket gets resolved quickly, it learns. When a customer churns, it learns. These feedback loops let the system continuously refine its decision-making.
That means your AI automation gets more accurate over time, not less. It adapts to seasonal trends, market changes, and your own business evolution—without you rewriting the rules.
Core AI technologies used in B2B automation
Several AI technologies power B2B automation, and understanding them helps you evaluate tools and solutions:
-
Machine Learning (ML): The system learns patterns from historical data to make predictions. Used for lead scoring, demand forecasting, customer churn prediction. It’s the backbone of most B2B AI automation.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): The system reads and understands human language—emails, support tickets, chat messages, contracts. This is how AI systems understand context from unstructured data.
-
Predictive Analytics: Using historical patterns, the system forecasts future outcomes. In sales: which leads will convert? In operations: how much inventory do you need next month? In finance: which invoices might be fraudulent?
-
Generative AI: Systems that create content—drafting emails, generating reports, writing contract summaries. This is newer but increasingly valuable for B2B automation, especially in marketing and sales outreach.
Real-world B2B context
Let’s ground this in what you’re actually dealing with:
-
Leads and pipelines: AI scores incoming leads in real time, predicts which will close, automatically triggers follow-up sequences, even identifies the next best action for each rep.
-
Invoices and payments: AI extracts data from PDF invoices in different formats, validates against purchase orders, flags discrepancies, routes to approval, and predicts payment timing.
-
Customer support: AI chatbots handle 65% of routine questions, route complex issues to specialists, and predict which customers are about to churn.
-
Content and marketing: AI optimizes ad spend in real time, personalizes email campaigns based on individual behavior, and analyzes attribution to show which touchpoints actually drive revenue.
-
Recruiting: AI screens hundreds of resumes, ranks candidates based on actual job requirements, and reduces hiring bias.
How AI Automation Works in B2B Companies (Step-by-Step)
Understanding the mechanics builds trust in AI systems. Here’s what actually happens:
Step 1: Data input
Your AI system connects to the sources where your business data lives: CRM systems (Salesforce, HubSpot), ERP systems (SAP, NetSuite), email servers, chat platforms, support tickets, payment systems. The system continuously ingests data—every customer interaction, transaction, and decision.
Step 2: AI model analysis and decision-making
The AI model (trained on historical data about successful and unsuccessful outcomes) analyzes incoming data in real time. It’s not following a script—it’s running mathematical models that identify patterns humans would miss.
Example: A lead arrives. The system analyzes 50+ signals simultaneously—company size, industry, website behavior, email engagement, LinkedIn profile changes, past interactions with similar companies. It compares against patterns in leads that converted and leads that didn’t. Then it produces a prediction: “This lead is 78% likely to close if contacted in the next 2 hours.”
Step 3: Automated action execution
Based on that analysis, the system executes the logical next action: trigger a personalized email, assign to the rep with the best historical close rate on similar leads, schedule a follow-up, or add to a nurture sequence. All without human intervention.
Step 4: Feedback loops and continuous learning
Here’s where AI automation becomes genuinely intelligent: the system tracks what happened next. Did the lead respond? Did it convert? How long did it take? That outcome feeds back into the model, updating the probability calculations for future similar situations.
After processing thousands of leads, the system’s accuracy compounds. Week 1, it might be 70% accurate. By month 3, it’s 85% accurate because it’s learned your specific market dynamics, your sales team’s strengths, and the real patterns in your data.
Where humans stay in the loop (important for trust)
This is critical: good AI automation doesn’t eliminate human judgment. It amplifies it.
Your sales reps still own complex deals. But instead of spending 3 hours on data entry and follow-up scheduling, they spend 3 hours actually selling. Your support team doesn’t disappear; they focus on genuinely difficult customer issues while AI handles the predictable ones. Your finance team stops manually reviewing invoices and spends time on strategy and exception management.
The best AI automation systems have a “human-in-the-loop” capability: they flag decisions they’re uncertain about for human review. If the system is only 55% confident about a lead score, it asks a sales leader to review it. That human feedback then trains the model to get better.
Key Benefits of AI Automation for B2B Businesses
The benefits cluster into five categories, each with measurable business impact:
Operational efficiency at scale
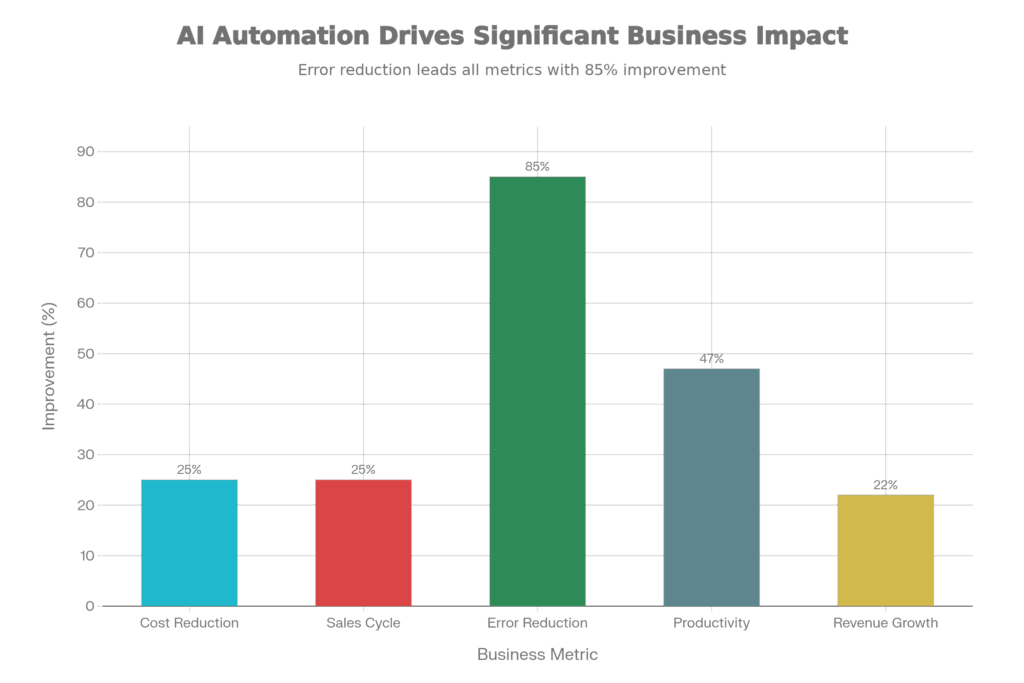
This is the most immediate benefit. Operational cost reductions of 20-30% are realistic within the first year. Why? Because AI handles the high-volume, repetitive work that scales linearly with your team size.
Imagine your finance team processes 2,000 vendor invoices monthly. At 10 minutes per invoice, that’s 333 hours—roughly two full-time salaries. AI-powered invoice processing cuts that to 2-3 hours for exceptions and review. You’ve freed up two salaries worth of capacity without firing anyone.
Extend that across every department—sales automation eliminating data entry, marketing automation optimizing ad spend, support automation deflecting routine tickets—and operational efficiency improvements compound. Companies report 49 hours of manual work eliminated per week per 50-person team.
Faster sales cycles
B2B sales is slow by nature. Buying committees. Multiple stakeholders. Complex decisions. AI shrinks the cycle at every stage.
AI-driven lead scoring identifies high-intent prospects in real time, so reps pursue the right opportunities. Automated follow-up sequences mean leads get touched at the right moments—never dormant, never over-contacted. Predictive analytics show which deals are likely to close soon, so reps can accelerate the right ones.
Real results: 25% shorter sales cycles. That’s massive. If your average deal is 90 days, that’s 22 fewer days. For a $50K average deal, that’s cash flow you get sooner.
Lower cost per lead and per customer
Your CAC (customer acquisition cost) is under pressure. AI automation reduces it through two mechanisms: finding more qualified leads (higher close rates = same cost for more revenue) and automating the nurturing and follow-up (lower cost per touch).
Companies using AI in lead generation see 50% more leads and appointments with same spend, because the system continuously optimizes targeting and timing.
Better decision-making with predictive insights
This is underrated. AI automation isn’t just about automation—it’s about seeing patterns humans miss.
Predictive analytics for pipeline health show you which deals are genuinely at risk and why. Demand forecasting uses real data instead of guesses, so you stock inventory efficiently. Churn prediction identifies customers who are about to leave before they do, giving your team time to intervene.
For revenue leaders, this means forecasts become reliable. For operations, it means less waste. For customer success, it means saving customers you would have lost.
Improved customer experience without hiring more staff
This is where AI automation creates a genuine competitive advantage for smaller companies. A SaaS company with 10 support staff can offer 24/7 support with AI chatbots handling routine questions and routing complex issues to humans. Your customers get instant answers. Your team handles what requires judgment.
Result: customers stay longer (improved LTV), satisfaction scores increase, and you didn’t double your headcount.
Competitive advantage for SMBs vs large enterprises
Here’s the non-obvious benefit: AI automation is actually more valuable for smaller companies than large ones.
Larger enterprises have the resources to hire specialized teams. You might hire a dedicated lead scoring person, a procurement analyst, a demand planner. Smaller companies can’t. But you can implement AI automation that handles these specialized functions at a fraction of the cost of hiring.
By implementing AI automation early, SMBs can punch above their weight. You can compete on speed and personalization against companies with 10x your headcount.
Core B2B Use Cases of AI Automation
Not all AI automation creates equal value. These use cases have the highest ROI because they’re either high-volume, high-impact, or both.
1. AI Automation in B2B Sales
AI automation in sales generates the most immediate ROI because sales is expensive and repetitive.
Lead scoring and prioritization
This is where most B2B companies start. Instead of reps manually scoring leads (educated guess) or using basic point systems (first-click attribution), AI analyzes all the data: company size, industry, decision-maker profile, engagement behavior, website activity, email opens, content downloaded, LinkedIn signals.
The result: accuracy jumps from 60% to 85% lead qualification rates. Your reps spend time on leads that actually convert instead of churning through lists.
Automated follow-ups and email personalization
Automation handles the timing and basic blocking. AI handles the personalization. The system knows your prospect researched your pricing page 3 days ago, downloaded a case study on Wednesday, and viewed your product demo video. It personalizes the follow-up: “I noticed you checked out our case study on [specific solution]—that’s exactly what helped [similar company] reduce costs by 40%.”
That’s not a template. That’s data-driven personalization at scale. 78% of B2B marketers use AI for this level of engagement optimization.
Sales forecasting and pipeline predictions
AI models look at your entire pipeline—not just the deals in stage 4. They see the patterns that predict closure: which deal characteristics, rep behaviors, and customer signals correlate with wins. Then they forecast revenue with accuracy levels that make CFOs stop asking “are you sure?”.
Better forecasts mean better planning, less panic at quarter-end, and better board meetings.
CRM data cleanup and enrichment
Your CRM probably has garbage data—duplicate records, outdated company information, missing phone numbers. This isn’t glamorous automation, but it’s valuable. AI identifies duplicates, standardizes company data, enriches records with current information, and flags data quality issues.
Clean data feeds into every other AI system. It’s table stakes.
2. AI Automation in B2B Marketing
Marketing automation is mature, but intelligent marketing automation is still underutilized.
Campaign optimization and A/B testing
Instead of you running tests and waiting for statistical significance, AI continuously runs A/B tests, identifies winners in real time, and automatically scales winners. Subject lines, send times, content variations, landing page layouts—the system tests and optimizes all of it.
Result: 10-20% improvement in sales ROI for companies using AI in this area.
Content personalization at scale
You can’t write personalized emails for 5,000 leads. AI can. It analyzes which content resonates with which personas, predicts the right content for each lead’s stage in the journey, and even generates personalized subject lines.
The effect on engagement: 35% increase in engagement rates.
Ad spend optimization
AI manages ad budgets across channels, platforms, and campaigns. It predicts which ad combinations work best for different audience segments, adjusts bids in real time, and pauses underperforming variations.
Companies that use AI for ad optimization see better ROI with the same budget.
Marketing attribution modeling
This is where most B2B marketers still guess. They look at last-click or first-click and assume that’s what drove the sale. AI multitouch attribution models analyze the entire customer journey and assign credit based on actual impact.
Example: a prospect sees your LinkedIn ad on Monday (5% impact), reads your blog on Tuesday (10% impact), watches a webinar on Friday (30% impact), and gets a demo the following week (55% impact). Traditional models credit only the demo. AI credit shows the real path to purchase.
This changes how you allocate budget. Some channels create awareness (lower direct attribution, high indirect value). Others drive conversion (high direct attribution). AI helps you optimize for revenue, not just leads.
3. AI Automation in Customer Support
This is where AI automation creates immediate cost and experience benefits simultaneously.
AI chatbots for B2B support
B2B support chatbots are different from consumer chatbots. They handle complex questions because B2B customers often have technical or process-specific issues. Modern AI chatbots can:
-
Answer questions about product functionality, pricing, and implementation
-
Generate quotes or identify the right product variant
-
Schedule demos or consultations
-
Route complex issues to specialist teams with full context
Real results: 65% of routine queries get resolved entirely by AI. Your support team doesn’t shrink—they focus on the 35% of issues that require real expertise.
Ticket classification and routing
Not all support tickets are equally urgent or complex. AI reads the ticket, understands what the customer is asking, and routes it to the right specialist—or routes it to self-service if the answer is in your knowledge base.
First-contact resolution rates improve 35% because the right person sees the ticket with the right context.
Predicting churn and customer issues
AI identifies customers showing signs of dissatisfaction before they churn. If a customer’s ticket volume spikes, or they’ve opened multiple critical issues, or engagement metrics drop—the system flags them. Your success team proactively reaches out instead of reacting to a churned customer.
Knowledge base automation
Instead of support writing articles from scratch, AI can generate documentation based on actual questions customers ask. It updates knowledge bases when you add new features. It even identifies gaps—questions your customers ask that your knowledge base doesn’t address.
4. AI Automation in Operations & Finance
This is high-volume, high-accuracy work—perfect for AI.
Invoice processing and reconciliation
Standard B2B operation: you receive an invoice as a PDF email attachment. Someone manually extracts invoice number, vendor, amount, line items. They check it against the PO. They route for approval. This takes 10 minutes per invoice.
At 2,000 invoices per month, that’s 333 hours. AI does this in 2-3 minutes per invoice by extracting data accurately, validating against POs, flagging discrepancies, and routing to the right person.
Cost reduction: 70-80% of processing time. Accuracy improvement: 99.99% vs human 85%.
Demand forecasting
Instead of forecasting based on last year’s sales plus your gut feeling, AI analyzes patterns in your data: seasonality, growth trends, market conditions, customer acquisition rate. It produces probabilistic forecasts that account for uncertainty.
For manufacturing and supply chain, this means less waste and fewer stockouts.
Fraud detection
AI continuously monitors transactions, procurement records, and payment patterns. It identifies anomalies: unusual vendor activity, duplicate invoices, suspicious payment patterns.
Financial services and healthcare B2B operations use AI fraud detection to catch problems in real time instead of finding them in audits.
Contract review and compliance checks
Reviewing contracts for legal issues and compliance is slow, expensive work. AI can:
-
Extract key terms from contracts
-
Flag unusual clauses or missing standard terms
-
Check against regulatory requirements
-
Identify risks (customer concentration, long payment terms, unusual liabilities)
Your legal team reviews AI analysis and recommendations instead of reading contracts from scratch.
5. AI Automation in HR & Recruiting
Recruiting is expensive ($4,000-$15,000 per hire in terms of time and tools), and quality matters hugely.
Resume screening
Recruiters spend days reviewing resumes. AI screens them in minutes, ranking candidates based on job requirements, experience, and actual qualifications—not just keyword matching.
Results: hiring process is 3-4x faster, and quality actually improves because the ranking is based on patterns in successful hires, not guesses.
Candidate matching
AI goes beyond resume screening. It matches candidates to roles based on cultural fit, growth potential, and likelihood of long-term success.
Employee engagement analysis
AI monitors engagement signals—survey responses, chat platform activity, calendar patterns—to identify flight risks before they leave and engagement gaps before they become cultural problems.
Workforce planning
Based on hiring patterns, attrition rates, project pipelines, and growth forecasts, AI can predict your staffing needs months in advance instead of scrambling to hire when you realize you’re short.
Popular AI Automation Tools Used in B2B (Tool-Based Search Traffic)
The tool landscape is crowded, but tools fall into categories. Understanding the categories helps more than memorizing tools (they change constantly).
CRM & sales automation tools
Salesforce Einstein, HubSpot AI, Pipedrive automation—these integrate AI directly into your sales process. They score leads, predict deal outcomes, and automate follow-ups within the context of your CRM.
Marketing automation platforms
HubSpot Marketing Hub, Marketo, Klaviyo—these automate email sequences, optimize timing, and personalize content. Modern platforms include AI for predictive analytics and content generation.
Workflow automation tools (Zapier-style + AI)
Zapier, Make, n8n—these connect tools and automate workflows. Modern versions include AI: “When a Stripe charge fails, analyze the reason and email the customer with relevant help content.”
AI agents and copilots
This is the cutting edge. AI agents are autonomous workflows that can execute multi-step processes: 6sense for account-based marketing, Salesloft for sales engagement, Sully for healthcare operations—these are AI agents that manage entire workflows.
Industry-specific AI automation software
Every industry is getting specialized AI tools. Legal tech companies use AI for contract analysis. Manufacturing uses AI for demand planning. Healthcare uses AI for claims processing. The benefit is domain-specific features that general tools can’t match.
Important distinction: don’t confuse the tool with the capability. The best AI automation isn’t always the biggest, most comprehensive tool. It’s the tool that solves your specific highest-impact problem first. You might use Salesforce for CRM, a point solution for invoice automation, and a workflow tool to connect them. That’s more flexible than forcing everything into one platform.
AI Automation vs RPA vs Traditional Automation (Comparison Section)
Understanding these distinctions prevents you from choosing the wrong tool for the job.
AI automation vs Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
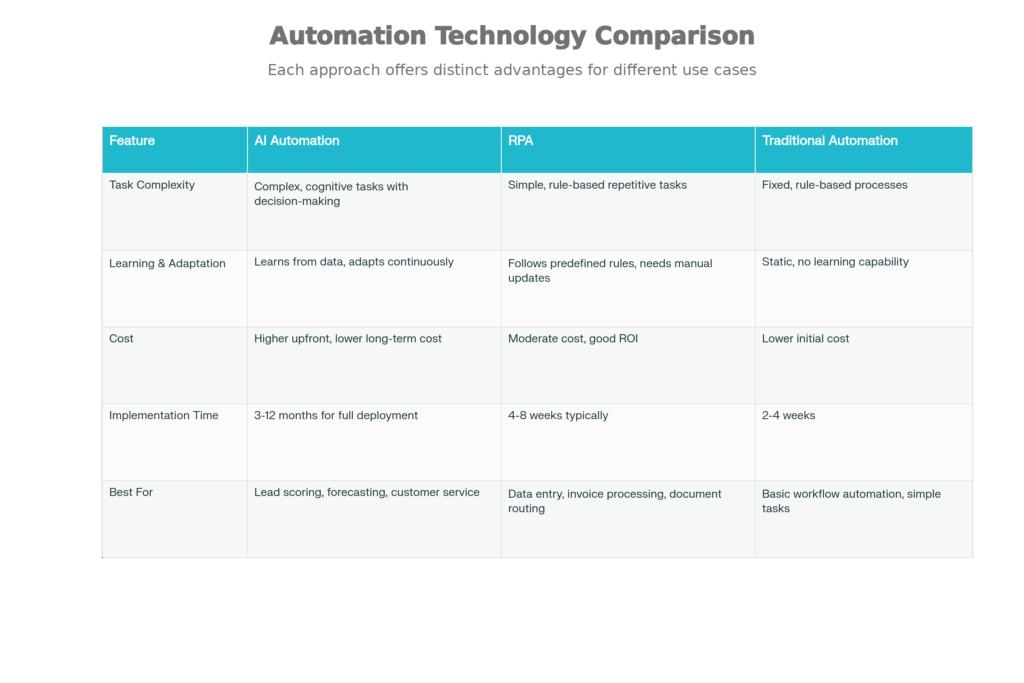
RPA and AI automation are often mentioned together, but they’re genuinely different:
RPA (tools like UiPath, Blue Prism) mimics human actions on computers. It clicks buttons, extracts data from forms, types information into systems. It’s fast—RPA can complete a task in 30 seconds that takes a human 30 minutes.
AI automation understands context and makes decisions. It looks at an invoice and knows if it’s fraudulent. It reads a customer email and understands the sentiment. It analyzes a sales conversation and predicts outcome.
Here’s when each makes sense:
-
RPA is best for: Clear workflows with structured data. “Extract these fields from form, paste into database, route to next step.” Great for processing applications, moving data between systems, automating repetitive data entry.
-
AI automation is best for: Complex decisions with unstructured data. “Read this customer email, understand the issue, categorize it, route to the right specialist, and draft a response.”
In practice, you often combine them. RPA handles the mechanical part (click approval button). AI provides the intelligence (understand if invoice is valid before routing).
AI automation vs no-code automation
No-code automation tools (Zapier, Make) let you chain actions together without coding: “When email arrives, extract attachment, upload to Google Drive, create record in CRM.” They’re powerful but limited.
If your workflow is: trigger → extract data → route to person → done, no-code is perfect.
If your workflow is: trigger → analyze situation → make decision based on context → execute different action depending on decision → learn from outcome → improve next time, you need AI.
When AI is overkill (important for credibility)
Not everything should be AI-automated. Some processes genuinely are best handled by humans or simple automation:
-
One-off processes that only happen occasionally don’t justify AI implementation
-
Processes with low volume and high variability might not have enough data to train an AI model effectively
-
Strategic decisions that require judgment and creativity should stay human
-
Processes where accuracy isn’t the constraint—if the problem isn’t data processing but human decision-making
Good AI automation implementation has this profile: high volume (1,000+ instances per month), repetitive, data-driven, and currently causing either cost or quality problems.
Hybrid automation models
The most powerful approach combines multiple technologies:
-
RPA for mechanical work: Bot clicks into legacy system, enters data
-
AI for intelligence: System analyzes invoice, determines if valid
-
Human for exceptions: Unusual cases flagged for human review and learning
This hybrid approach combines the speed of RPA, intelligence of AI, and judgment of humans. It’s the model most mature companies move toward.
How to Implement AI Automation in a B2B Company (Practical Guide)
Implementation matters as much as the technology. You can buy the best tool and fail with poor execution. Here’s how successful companies do it:
Step 1: Identify High-Impact Processes
Not all processes are created equal. Your first implementation should be:
-
Repetitive + data-heavy: Task done thousands of times monthly with clear data inputs
-
Bottleneck: Currently slowing down teams or causing quality issues
-
High impact: Success means significant cost savings or revenue improvement
Good candidates:
-
Lead scoring in sales (high impact, high volume, data-driven)
-
Invoice processing in finance (high volume, clear data, measurable ROI)
-
Customer support ticket routing (high volume, repetitive, clear impact)
Bad candidates (don’t start here):
-
CEO’s calendar management (low volume, high variability, low impact)
-
Quarterly strategy sessions (low volume, too much judgment required)
-
Hiring C-level executives (low volume, high-stakes, human judgment essential)
Score opportunities on three dimensions:
| Dimension | Scoring | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Current Volume | Monthly instances processed | 500-10,000 = good, >10,000 = excellent, <500 = probably not ready |
| Current Cost/Impact | Monthly cost to process or revenue impact of delays | $10,000+/month = definite candidate |
| Data Maturity | Quality and completeness of historical data | Clean, complete data = ready; messy data = requires preparation |
Step 2: Prepare Your Data
This is unglamorous and often underestimated. Good AI automation requires good data, and most companies have messy data.
Why clean data matters more than tools
You can have the most sophisticated AI model ever built, but if you train it on garbage data, it produces garbage predictions. Gigo (garbage in, garbage out) is real.
Before you implement, you need to assess data quality across several dimensions:
-
Accuracy: Are values correct, or are there systematic errors?
-
Completeness: Are required fields filled in, or are there patterns of missing data?
-
Consistency: Is data formatted consistently across systems? (Dates as MM/DD/YYYY or DD/MM/YYYY? Company names with or without legal suffixes?)
-
Integrity: Does data make logical sense? (Customer acquired in 2022 but marked as signed up in 2020?)
Common B2B data mistakes
-
Duplicate records: Same customer appears three times under slightly different names
-
Incomplete data: 40% of company records missing revenue or employee count
-
Inconsistent formats: Phone numbers sometimes (555) 123-4567, sometimes 555-123-4567
-
Historical inconsistency: Definitions of “qualified lead” changed twice in the past year, making historical patterns unreliable
-
Data silos: Lead engagement data lives in marketing system, sales data lives in CRM, company data lives in a spreadsheet—they don’t talk
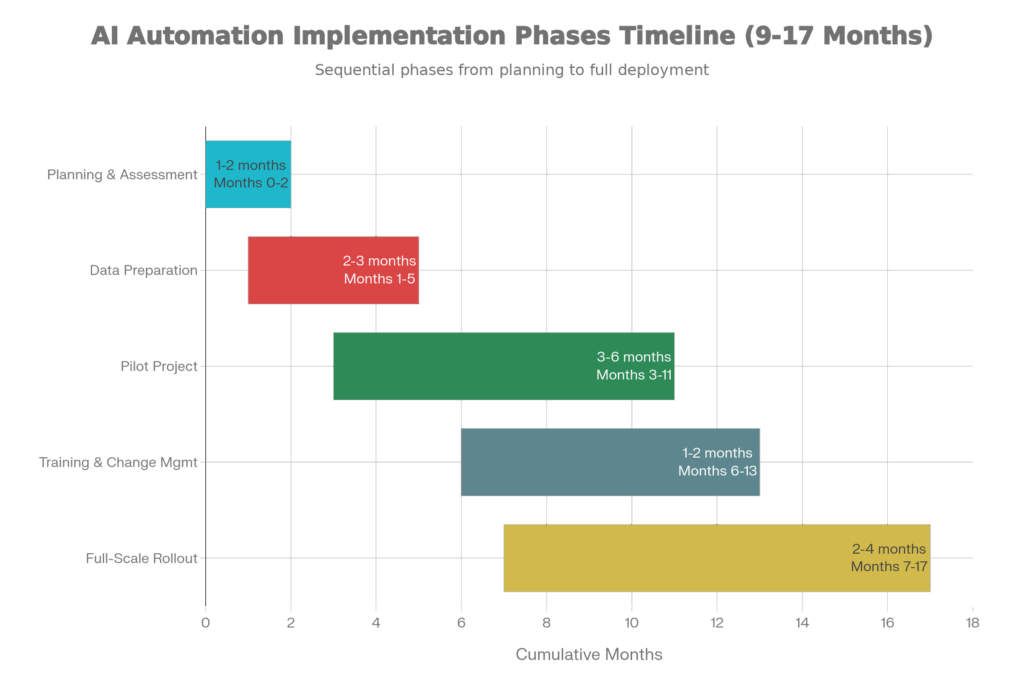
Solution: implement data preparation as a formal step. Allocate 1-2 months (for mid-market companies) and a small team to:
-
Identify and merge duplicates
-
Standardize formats and values
-
Fill missing data where possible (using external data sources)
-
Document how data has been defined and collected over time
-
Create data governance rules for the future
This investment pays dividends. Bad data = model fails = you blame the AI. Good data = model succeeds = AI delivers value.
Step 3: Choose the Right AI Automation Approach
Off-the-shelf tools vs custom AI
Off-the-shelf tools like HubSpot’s predictive lead scoring or Salesforce Einstein are purpose-built, cheaper, faster to deploy. You trade some customization for faster implementation.
Custom AI (building with a vendor or in-house team) takes longer and costs more but can be perfectly tailored to your specific business logic.
Decision framework:
-
Off-the-shelf if: Your workflow matches the tool’s use case well enough. 80% match is good enough.
-
Custom if: Your workflow is unusual or requires proprietary business logic
-
Hybrid if: Use off-the-shelf for 80% of cases, custom for edge cases
Build vs buy decision
This is simpler: unless you’re a large tech company with in-house AI teams, you should buy or partner with a vendor, not build.
Building AI automation requires:
-
Data science team (expensive: $200K-$500K/year per person)
-
ML engineers to productionize models
-
Infrastructure (cloud compute, data pipelines)
-
Ongoing maintenance and model updating
Buying or partnering means paying for the tool and implementation, but you’re leveraging the vendor’s expertise.
Cost comparison for a mid-market company implementing lead scoring AI:
| Approach | Year 1 Cost | Time to Value |
|---|---|---|
| Build in-house | $500K-$1.5M | 6-12 months |
| Buy tool + implementation | $50K-$200K | 3-6 months |
| Partner with AI vendor | $100K-$300K | 2-3 months |
Step 4: Start Small, Then Scale
The biggest implementation mistake: thinking too big and building something that never goes live.
Pilot projects
Start with a narrowly scoped pilot: one department, one specific workflow, 1-3 months. For example:
-
Sales team pilots AI lead scoring on new inbound leads only (not existing leads, not outbound)
-
Finance pilots invoice automation on one vendor category first (maybe just software/cloud services)
-
Support pilots chatbot for one product line (maybe just your API documentation questions)
Scope it small enough that you can finish in 2-3 months and measure results cleanly.
Measuring early wins
Before you implement, decide what success looks like:
For lead scoring:
-
Current: 60% of reps’ time is spent on low-quality leads
-
Goal: Reduce time spent on low-quality leads to 20%
-
Measurement: Sales rep survey + CRM data on lead quality
For invoice processing:
-
Current: 2,000 invoices/month, 10 min each = 333 hours
-
Goal: Reduce to 1 hour total (exceptions only)
-
Measurement: Processing time per invoice, error rate
Measurement matters because it justifies expansion to other departments.
Step 5: Train Teams and Set Governance
AI automation changes how people work. Your CRM analytics person now manages AI model performance instead of running reports. Your support manager now monitors chatbot conversations to find knowledge gaps instead of assigning all tickets manually.
Change management
People resist things they don’t understand. You need:
-
Clear communication about why this change is happening (cost reduction, better customer experience, let humans focus on complex work)
-
Training on how to use the new system
-
Early involvement of affected teams (don’t surprise people with a new system)
-
Support during transition (don’t blame people when they struggle with new workflow)
-
Patience: productivity drops 15-25% during adaptation, then recovers and exceeds baseline
Ethical and compliance considerations
AI makes decisions, which creates responsibility. You need:
-
Explainability: When AI rejects an invoice or deprioritizes a lead, someone should be able to explain why
-
Bias review: Is the AI treating customers or vendors fairly, or are there hidden biases in the training data?
-
Audit trails: For compliance, you need records of how decisions were made
-
Human override: High-stakes decisions should have human sign-off
For B2B operations, this usually means:
-
AI can auto-approve invoices up to $5,000 if it’s confident
-
AI can deprioritize leads but humans still see them
-
AI routes support tickets but humans decide if routing was wrong
-
Document why model made each decision for audit trails
Real Examples of AI Automation in B2B
These aren’t hypothetical. These are patterns from real companies:
SaaS company improving lead conversion
A B2B SaaS company selling to mid-market tech teams implemented AI lead scoring. They:
-
Analyzed 18 months of historical lead data: 50,000 leads, 850 converted
-
Identified patterns: company size, industry, decision-maker title, content engagement predicted conversion better than source
-
Built model on historical data, applied to new leads
-
Result: Sales team prioritized AI-ranked leads, sales cycle dropped 25%, revenue increased 22% in 6 months
-
Scale: After success, expanded to account-based marketing personalization
The key: they started with clear data (lead source, company info, engagement), clear outcome (converted or not), and clear action (prioritize which leads to call).
B2B service firm reducing support workload
A professional services firm (150 employees) was drowning in support requests—clients calling with basic questions about project status, billing, or how to use the platform.
They implemented an AI chatbot that:
-
Answered questions about project timeline (connected to project management system)
-
Explained billing items (connected to finance system)
-
Generated reports and documentation
-
Routed complex issues to humans
Result: 65% of requests resolved without human involvement, support team went from 8 people to 4 people (not fired—redeployed to strategy and customer success), customer satisfaction increased (clients got faster answers).
Manufacturing company improving demand forecasting
A manufacturer of industrial components traditionally forecast demand using last year’s sales plus gut feel. This led to both stockouts and excess inventory.
They implemented AI demand forecasting that:
-
Analyzed historical sales by SKU, customer, season
-
Included external factors (economic indicators, construction spending)
-
Produced probabilistic forecasts (not just one number, but range)
Result: 30% reduction in excess inventory, 40% reduction in stockouts. For a company with $100M in inventory, that’s millions in working capital freed up.
Agency automating client reporting
A marketing agency generated 30+ client reports monthly. Each one required pulling data from multiple systems, creating slides, writing analysis. Each report took 3-4 hours.
They implemented generative AI that:
-
Automatically pulls data from Google Analytics, Meta, LinkedIn, ad platforms
-
Generates draft analysis and recommendations
-
Creates slides in client brand
-
Human strategist edits and personalizes
Result: Report generation time dropped from 3 hours to 30 minutes. Agency could serve 3x more clients without hiring. Clients got reports faster. Strategists focused on strategy instead of data processing.
ROI of AI Automation for B2B: What Results to Expect
ROI is why you’re implementing AI. Here’s what realistic expectations look like:
Cost savings vs revenue impact
Most AI automation delivers value through both cost savings and revenue impact:
-
Cost savings: Operational efficiency. Reducing invoice processing time saves salary cost.
-
Revenue impact: Speed and personalization. Faster sales cycles mean you close more deals. Better customer experience means higher retention.
Cost savings is easier to measure and happens faster (0-6 months). Revenue impact takes longer (3-12 months) but is often larger.
Short-term vs long-term ROI
-
Months 0-3: No value. You’re paying for implementation, data preparation, training. Ignore ROI during this period.
-
Months 3-6: You see early benefits from pilot projects. First cost savings appear. ROI is probably 50-150% on pilot investment.
-
Months 6-12: Full scale realized. You’ve rolled out to the whole team, optimized the process. ROI is 200-400% on full investment.
-
Year 2+: Compounding. Model improves with more data. You expand to other processes. ROI grows 500%+.
McKinsey reports: companies that implement AI see 1.5x faster revenue growth and 1.4x higher return on invested capital over 3 years compared to non-adopters.
KPIs to track
These are the metrics that matter for your business:
For sales automation:
-
CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost): Total sales and marketing spend / new customers. AI can reduce by 15-25% through more efficient lead prioritization.
-
LTV (Lifetime Value): Total revenue from customer – cost of serving. Improves when AI helps close better customers.
-
Sales cycle length: Days from first touch to close. AI reduces by 20-30%.
-
Quota attainment: Percentage of reps hitting quota. Increases when top performers focus on real opportunities.
For operations:
-
Process cost per instance: Cost to process one invoice/support ticket/contract. AI can reduce 50-80%.
-
Accuracy rate: Percentage of decisions correct (invoices approved that shouldn’t be, for example). Improves with AI.
-
Throughput: Instances processed per month. Increases without adding headcount.
For customer experience:
-
CSAT (Customer Satisfaction): How happy customers are. Improves with faster response and personalization.
-
Churn rate: Percentage of customers who leave. Improves with better support and proactive engagement.
-
NPS (Net Promoter Score): How likely to recommend. Improves with better experience.
Track these before and after implementation. You should see movement within 6 months.
Challenges and Risks of AI Automation in B2B
Not everything about AI is rosy, and you should know the pitfalls.
Data quality issues
We mentioned this, but it deserves emphasis. Companies implementing AI without addressing data quality fail. Frequently.
Symptoms: The AI model predicts with 55% accuracy (better than random, but not better than a human). Costs exceed benefits. Leadership loses faith.
Prevention:
-
Treat data preparation as a separate, funded project
-
Implement data quality checks before any AI training
-
Plan for 20-30% of implementation cost to go to data work, not tools
Over-automation risks
It’s tempting to automate everything. Don’t.
If you automate all customer interactions without human oversight, and the AI makes an error, you’ve harmed that customer at scale. If you automate all hiring decisions, you’ve built in whatever biases exist in your historical hiring data.
Smart automation: humans stay in the loop for high-stakes decisions, exceptions, and cases the AI is uncertain about.
AI bias and errors
Your AI model only knows what it learned from historical data. If your historical data has biases, your model will perpetuate them.
Example: You train lead scoring on leads from the past 2 years. During that period, your company was acquiring mostly tech companies on the West Coast. Your model learns tech+West Coast = higher score. Now it systematically undervalues East Coast prospects and different industries, even though market conditions have changed.
Prevention:
-
Review training data for biases explicitly
-
Regularly audit model performance by segment (does it score women and men similarly?)
-
Use AI to reduce human bias (like hiring AI that evaluates resumes more objectively than human hiring managers), but don’t blindly trust AI
Security and compliance concerns
AI models require access to data—customer data, financial data, sensitive information. You need:
-
Security: Proper access controls, encryption, audit logs
-
Compliance: If regulated (healthcare, finance), AI systems need to comply with regulations
-
Data privacy: GDPR, CCPA and other regulations restrict how you use personal data
If you’re in regulated industry, plan to spend extra on compliance work. It’s worth it.
Employee resistance
People worry: “Is this AI going to replace me?”
The answer is usually no—the AI replaces the repetitive parts of the job, not the job itself. But you have to communicate this clearly and manage transition thoughtfully, or talented people leave.
Address this:
-
Be transparent about what’s automating
-
Emphasize how this changes jobs, not eliminates them
-
Retrain people for higher-value work
-
Involve people in implementation early
AI Automation for B2B by Industry
SaaS companies
SaaS is early to adopting AI automation:
-
Lead scoring and sales automation (already widespread)
-
Product usage analytics (churn prediction, expansion opportunities)
-
Customer success automation (onboarding workflows, proactive support)
-
Billing and usage tracking (auto-scaling, usage-based billing)
Manufacturing
Efficiency focus:
-
Demand forecasting (reduce inventory waste)
-
Predictive maintenance (minimize unplanned downtime)
-
Quality control (AI detects defects in manufacturing)
-
Supply chain optimization (route planning, supplier management)
Healthcare B2B
Compliance + operations focus:
-
Claims processing (extract data, validate, process)
-
Fraud detection (unusual billing patterns)
-
Appointment scheduling (coordinate across providers)
-
Documentation automation (e.g., reducing physician documentation burden, though this is evolving carefully due to compliance concerns)
Healthcare implementation is slower due to regulation (HIPAA), but the payoff is high.
Finance and fintech
Risk and accuracy focus:
-
Fraud detection (transaction monitoring, unusual patterns)
-
Underwriting (evaluate risk, approve/deny loans)
-
Compliance (AML/KYC reporting, regulatory requirements)
-
Portfolio management (prediction of asset performance)
Professional services
Knowledge and staffing focus:
-
Utilization optimization (assign best person to each project)
-
Time tracking and billing (AI infers activity when employees forget to log time)
-
Client profitability analysis (which clients are actually profitable?)
-
Knowledge management (document tribal knowledge, make available to team)
E-commerce B2B
Conversion focus:
-
Product recommendations (suggest complementary products)
-
Pricing optimization (dynamic pricing based on demand, inventory, customer segment)
-
Demand forecasting (stock the right products)
-
Returns and fraud (detect fraudulent returns or orders)
Each industry has different AI automation priorities based on what drives profitability and what creates the biggest pain point.
Future of AI Automation in B2B
Where is this heading? Three trends to watch:
AI agents replacing entire workflows
We’re moving from “AI helps humans do tasks” to “AI autonomously executes workflows.” An AI agent for sales might:
-
Monitor inbound opportunities
-
Qualify them based on fit
-
Route to the right sales rep
-
Create follow-up tasks
-
Send personalized outreach
-
Track engagement
-
Identify the next best action
All without human intervention for qualified leads.
This isn’t science fiction. Companies like Salesforce, 6sense, and Salesloft are shipping AI agents now in 2025. Expect 30-40% of B2B workflows to be AI agents by 2027.
Autonomous sales and support systems
For simpler sales cycles and standard support issues, AI handles the entire interaction. Customer initiates conversation, AI:
-
Understands the need
-
Provides options
-
Answers questions
-
Closes the deal or routes to human if needed
-
Handles post-sale support
For transactional B2B sales (e.g., SaaS contract renewals, standard services), this is increasingly viable.
Vertical-specific AI automation
Right now, most AI tools are horizontal (work across industries). The future is vertical: AI tools built specifically for healthcare B2B, manufacturing, real estate, etc., with industry knowledge built in.
This means:
-
Faster implementation (tool understands your industry)
-
Better accuracy (trained on your industry’s data)
-
Better compliance (regulatory requirements built in)
-
Higher cost per industry (less scale)
Human-AI collaboration models
The mature model isn’t “AI does everything” or “humans stay in charge.” It’s collaboration: humans handle strategy, judgment, creativity, and exceptions. AI handles execution, pattern recognition, and volume.
Sales rep and AI work together: Rep decides strategy for an account. AI executes outreach, tracks engagement, flags when the account is ready for human contact. Rep closes the deal. AI handles renewal.
Finance team and AI work together: Team sets approval rules. AI routes invoices, flags exceptions. Team decides how to handle exceptions. AI learns from those decisions and improves.
This collaboration is where the real value lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI automation in B2B?
AI automation uses machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive analytics to automate business processes that require decision-making, not just rule-following. Unlike traditional automation that follows if-then rules, AI automation learns from data, adapts to new situations, and improves over time.
Is AI automation expensive for small B2B companies?
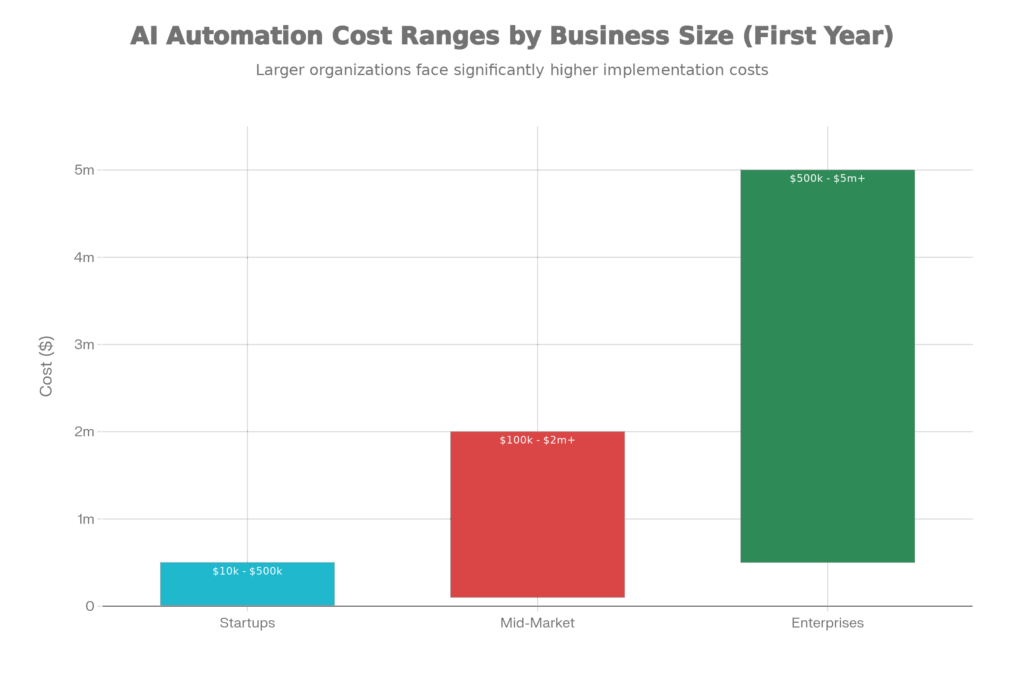
Implementation starts at $50K-$150K for smaller companies ($10K setup on up through implementation and ongoing support). Mid-market companies typically invest $100K-$500K in year one. But the ROI is real: average operational cost reduction of 20-30%, often within 6-12 months. For most companies, payback is 1-2 years.
How long does it take to implement AI automation?
For mid-market companies, pilots take 3-6 months, full-scale implementation 9-18 months. This includes planning, data preparation, pilot, training, and rollout. Speed depends on data quality and complexity of the process being automated. Fast implementation: 2-3 months for simple processes with clean data. Slow implementation: 12+ months for complex processes across multiple legacy systems.
Does AI automation replace jobs?
AI automation replaces repetitive task components, not jobs. A support specialist doesn’t disappear; they handle complex issues instead of simple ones. A sales rep doesn’t disappear; they focus on sales strategy instead of data entry. In studies, AI automation shifts roles but doesn’t eliminate headcount—it frees people to work on higher-value activities.
What’s the difference between AI automation and AI agents?
AI automation solves specific tasks (score leads, process invoices, route support tickets). AI agents execute entire workflows autonomously (manage the entire lead-to-customer journey or the entire support experience). Agents are more advanced and are becoming more common in 2025.
Final Thoughts
Who should adopt first
If you’re:
-
Drowning in repetitive work consuming 20%+ of team bandwidth
-
Operating with data-heavy processes and incomplete visibility
-
Facing competitive pressure from companies with better speed or personalization
-
Dealing with high-volume, high-value operations where errors are costly
You should start now. Not later. Now. The advantage compounds—companies implementing AI now will have 18+ months of advantage over companies starting in 2026.
Mistakes to avoid early
-
Choosing the wrong first process: Pick something with clear data, high volume, and measurable ROI. Not your CEO’s calendar.
-
Underestimating data preparation: Plan for 20-30% of time and budget to go to data work. You’ll be glad later.
-
Ignoring change management: Implementing the tool is 20% of the work. Getting people to use it effectively is 80%.
-
Over-automating: Automate the repetitive 80%, but keep humans in the loop for complex 20%.
-
Not measuring early wins: You won’t get funding to expand if you can’t prove the pilot worked.
Simple starting point for most B2B teams
Pick one of these based on your function:
-
Sales: Implement AI lead scoring in your CRM. Should take 8-12 weeks, cost $25K-$75K, and show 15-25% improvement in lead quality within 3 months.
-
Operations: Implement AI invoice processing. Should take 8-12 weeks, cost $15K-$50K, and show 50-70% reduction in processing time within 2 months.
-
Marketing: Implement AI email optimization. Should take 6-10 weeks, cost $10K-$30K, and show 10-20% improvement in open/click rates within 4 weeks.
-
Support: Implement AI chatbot for common questions. Should take 6-8 weeks, cost $10K-$25K, and deflect 40-60% of routine tickets within 2 weeks.
All of these have clear ROI within 2-3 months, manageable implementation, and can be done without massive data preparation.
Encouraging but realistic close
AI automation isn’t magic. It won’t fix fundamental business problems or broken processes. What it does do is take the painful manual work out of good processes and make them better—faster, cheaper, with fewer errors.
Your lead scoring probably isn’t bad. But it takes too long and relies on guesswork. AI makes it 80% accurate and real-time.
Your support isn’t failing. But you have 20 routine questions you answer every day. AI answers them so your team focuses on the problems that need human judgment.
Your operations work, but they tie up people who could be doing strategic work. AI does the volume so people do the strategy.
This is where the real competitive advantage lives. Not in having smarter people or more money. In making the good systems you already have faster, cheaper, and smarter.
Start small. Measure carefully. Learn from the pilot. Then expand. You don’t need to automate everything immediately. You need to start automating the things that matter most.
The companies that do this in 2025 will have 18 months of compounding advantage by the time this becomes table stakes in 2027. Make the decision to start now.